What Is VoIP & Why Is It So Popular?
So what is VoIP? It’s an acronym for Voice over Internet Protocol, or Voice over IP. It is a type of Internet powered telephony or Internet powered voice communication. Simply, VoIP means ‘voice service over the Internet’. VoIP today is used widely by people and businesses. Business VoIP is such a popular technology as voice calls can be made completely free and without the use of a physical telephone at all, via apps, computers / laptops, tablets or phones. So it’s both cost efficient and widely available. Some familiar uses of hosted VoIP technology today include; Skype, WhatsApp and unified communications solutions, such as our metricVOICE offering.
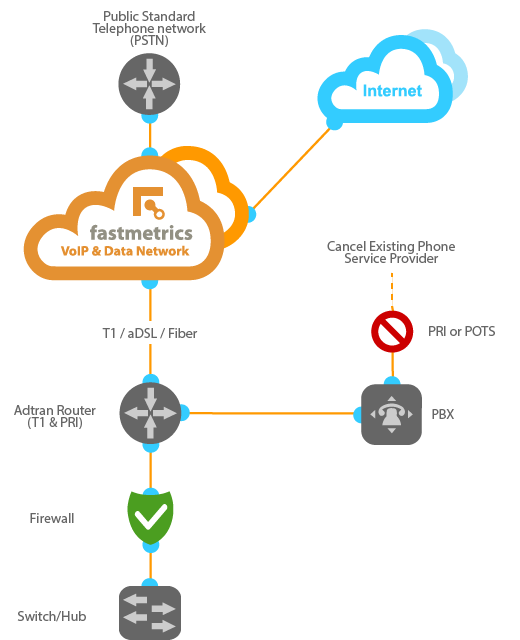
Fastmetrics Hosted Voice & VoIP Service Setup Diagram
As displayed in the hosted voice diagram below, the major difference between Fastmetrics voice service and other VoIP services, is that we manage our own private voice network. This means that your voice traffic never travels on the public Internet. This has both Quality of Service (QoS) and security benefits. Our voice team has the ability to apply VoIP service to any existing phone system.
How Does VoIP Work?
To find out more about what VoIP actually is and how VoIP works in a business or an enterprise environment, we recommend the below video from Eli The Computer Guy. Eli takes a take deep dive into all you need to know to educate yourself on VoIP communications, requirements and hardware.
Video transcript: Hello again! As you know I’m Eli the Computer Guy over here for Everyman IT. And today’s class is Introduction to VoIP or Introduction to Voice Over IP. So Voice over IP is one of the latest and greatest and most wonderful technologies. Really, it has been around or it has been pushed out for commercial use in about the last 10 years. This class today is going to be a foundation for understanding VoIP within a business or enterprise class environment. So if all you want to do is set up some little Skype phone and talk to somebody, your neighbor a state away or your girlfriend, boyfriend, husband, or wife, this class is going to tell you much more than you need to know.
This class is going to be about the fundamental concepts so if you want to connect a business to Voice over IP. We are going to be talking about VoIP servers, VoIP clients, things called hard phones and soft phones. We are going to talk about gateways. We are going to talk about protocols. We are going to talk about codecs. We are going to talk about latency and quality of service and basically, the foundation concepts. So if you are looking at migrating an entire business whether they’re five people or a thousand people to a Voice over IP system, we are going to talk about the basic concepts of what you need to know.
Introduction to VoIP
Again, if all you want to do is go out and buy some little Skype phone or download Skype, this is probably way too much for you. This is for Voice over IP in the business or enterprise class world. So give me a second. Let me get a few things together and then we are going to go into a class, Introduction to Voice over IP. So the first thing that we need to talk about is VoIP or Voice over IP servers or you may also hear them termed IP PBXs. So Voice over IP servers are the main servers that route your calls through Voice over IP phones or devices.
So we talk about in the Introduction to Telephone Class and all that where a normal phone system has a PBX. So within your building, you have a PBX, right? And from this, all your telephones, your call boxes, your auto attendants, everything goes through this PBX. So all your phones, everything go back to this. Well, the nice part is we are now dealing with a networking world. So this is for a telephone system. Now remember, when we are talking about Voice over IP, we are not talking about telephones. We are talking about data devices that transmit real-time audio communication. As we go further in this track, this is going to become more and more important. Like I say, right now you may think I’m splitting hairs between a telephone system and a data system that transmits real-time audio communication.
But when you get into legal aspects of the difference between a telephone and a data system, these are huge. Congress, local legislatures, etc have mandated a whole hell of a lot of laws about how a telephone system has to work. They haven’t mandated any or very many laws on how an instant messaging system that also happens to trail and transmit real-time audio communications should work. So it’s very important.
Like I say, when I keep talking about the difference between a telephone system and a data system with real-time audio communication, this really does matter and this really, really does matter in the real world like when you are dealing with businesses and enterprises. If you are just dealing like I say, with your little home phone and maybe one Skype handset in your house, probably doesn’t matter. But in the business world, it really does matter.
Voice over IP (VoIP) Servers
So the first thing to understand with these Voice over IP servers or what are sometimes called IP PBXs is of course the use of the TCP/IP Ethernet Network. So basically, all of your phones, the PBX, et cetera is going to use Ethernet and it’s going to use TCP/IP to communicate. So now instead of having a telephone PBX with phones and everything in their own world, you now have a phone system that resides on the same network as everything else. So you use routers. You use switches. You use TCP/IP. You use computers, etc. So this is very important.
We are now going to talk about the client systems in a moment. When we are talking the telephone, we are talking the telephone world, the Introduction to Telephone Class, we talk about stations. We are now talking about the Voice over IP world and so we are going to be talking about clients. Again, another very important thing once you really understand what’s going on.
So the huge thing with this Voice over IP server and the other reason I keep calling it a Voice over IP server is if you’ve taken the server classes, you will know that a server is any computer that provides services to other computers on the network. So this is a Voice over IP server. Like I say, some people call them IP PBXs. I would argue that it’s not technically correct. This is a server for real-time communications. So Voice over IP servers, so with this, this server will connect into your switch like normal and then this will connect into your router like normal. The router will then connect off into the internet. Now, all your telephones or clients on the system will then connect to the switch and that is how they will connect to this Voice over IP server.
Now, there are a couple of interesting things to think about with this Voice over IP server, is the first is you can have your client computers or your client telephones connect to the Voice over IP server through the normal networks. So you have a router, you have a switch, etcetera. You can also have analog or digital ports connected to the Voice over IP server. So some of these Voice over IP servers you will actually be able to plug a normal telephone straight into it.
So let’s say you bring in your telephone from home, some of these Voice over IP servers you could plug that home telephone straight into the Voice over IP server. It depends on whether or not they have the little plugs to allow you to do that. So if you need to plug in digital phones or analog phones, whatever Voice over IP server you buy, make sure it has that functionality. So with Voice over IP servers, mainly, all the communications happen over your normal Ethernet network, TCP/IP, IP Protocols, etc. But if they have these little ports on here, they can also connect normal phones but they’ve got to have those little ports.
The next thing is as we talked about before in the other classes is trunk lines. So how do you call in and how do you call out from a Voice over IP server? Now, the first way you can do it is if you are doing completely Voice over IP. You can have something called a Voice over IP trunk from a provider. So you have a provider, this is not Verizon, it’s kind of like – it’s like a company called OnSIP. There are companies out there that will provide you IP trunk lines. So you don’t need normal telephone lines anymore. You can actually get all of your calls straight through the internet. So these companies will provide you a Voice over IP trunks.
So the way calls can come in and out are either through the internet, you have one of these providers that your Voice over IP trunk and so what happens is when you go to call out, your little phone connects to the Voice over IP server, the Voice over IP server then connects to those Voice over IP trunks, or on your Voice over IP server you can have connections that can connect you to normal phone lines off from the outside world. So like I say here in Baltimore, we use Verizon for our phone company.
But whatever phone company you use, they have their little phone line and again if your Voice over IP server has the right plugs, you can plug one of these phone lines from your telephone company into the Voice over IP server and then when somebody makes a call, the call goes through your network, to the Voice over IP server and then goes out that normal trunk line. So this is a normal telephone line that goes out to the outside world. So this is the first way a Voice over IP server can work. So in this model, your Voice over IP server basically replaces the PBX that you would have before. So before, you had a special electronics device called a PBX that routed all your telephone communications. Now, you have a Voice over IP server, all your Voice over IP devices connect to it and then it is the one to route calls out to the outside world.
Now, here is something that’s really, really cool and one of the most wonderful things in the world about the Voice over IP system is now that we are doing everything over IP, now that we are doing everything over an Ethernet network, this Voice over IP server no longer has to be in our building. So you can actually have your Voice over IP server hosted on the outside world.
So over here out in the internet, just like you would have an email server out on the internet, you can have the Voice over IP server out here. And basically, you rented this from a company. Let’s say the company like OnSIP or other ones, they will host your Voice over IP server for you. So you have all of your telephones in the building, all your computers, telephones, etc. They connect to the switch, the switch connects to the router, and then they all connect to this Voice over IP server that’s no longer even in your building. Why? Because everything now uses TCP/IP and Ethernet networking standard.
This is a great and wonderful thing because PBXs whether they are normal PBXs, normal telephone PBXs or whether they are Voice over IP servers, cost a lot of money. For a basic Voice over IP server that you’re going to put into a business, it’s going to cost $2,000 just for the server and then you add in your phone lines that you have to pay for and add in all these other stuff and it gets to be very expensive.
Well, now that you can pay for a simple Voice over IP service, you just pay $25 or $50 or whatever it is per month per phone and you no longer have to worry about that box sitting inside of your building. So this is one of the very, very, very great wonderful things about this Voice over IP service. You get the whole enterprise class functionality, all the phone lines, everything, it all works but it’s all now out in the internet just like Gmail is, just like Hotmail, just like all of those things. You no longer actually have to buy the box for that Voice over IP server.
So this is a brief introduction to the Voice over IP servers. Like I say, we will have more classes so we flesh all of this out. These Voice over IP servers, they can be manufactured by normal companies or companies that you probably heard of like Avaya or Lucent or AT&T of Nortel, Mitel, etc. And those are proprietary Voice over IP servers or IP PBXs. Or they now have new companies out such as Asterisk or it’s called sipX. These are free open source Voice over IP servers that basically as long as you know how to install them and set up a computer, you can have a completely free enterprise class Voice over IP server for the cost of a computer that was in the corner collecting dust. So that’s pretty cool.
So these Voice over IP servers, I mean they act like the PBXs that we’ve talked about. They route all the communications, they contain the auto attendants, they contain the call trees, they contain the call paths, the hunt groups, et cetera. So they do all the routing that the normal old PBXs did. The difference is, is they communicate using Ethernet and TCP/IP versus the old phone lines that the old PBXs did.
Again, the reason that this is very important is you can have the Voice over IP, PBX, or server inside your building or you can simply pay for the service for somebody else to deal with it. So all these telephones and such will communicate out to that server in the outside world. This is a very, very huge, important thing. And again, like I say, if you want to experiment like when we get to the end of this and you want to experiment with Voice over IP a little bit, not only can you buy servers, again from Avaya and such, but you can buy free completely or I guess not buy that, you can get completely free open source Voice over IP solutions. Again, there’s Asterisk, there’s Switchvox, and there’s something called a sipX. I’ll put links to it at the bottom of this at the end. But this is a Voice over IP server.
So we talked about the Voice over IP server. So we have our VoIP server over here. And remember, this is a server. This is a computer that provides services to other computers on the network. Remember, that’s what a server is. Although people call it like an IP PBX and all that garbage, it’s really a server. It’s really Voice over IP server.
So all of your devices or clients because remember, since it’s a server clients connect to servers, are going to connect to this Voice over IP server. So whether it’s a telephone, whether it’s a computer that allows you to make calls, whether it’s your little iPhone, whatever it is, if it is a device and it’s going to deal with your Voice over IP communications, it’s going to go back and it’s going to talk to the server.
What are the differences between a VoIP ‘hard’ phone and ‘soft’ phone?
Now when we are talking about the devices and we are talking about clients, you are going to hear two terms said a lot, and that is going to be hard phones and soft phones. So what is the difference between those two things?
A hard phone is a telephone. It looks like a telephone. It looks like a telephone that you would think is a telephone. It’s grey or it’s white or it’s black. It’s has got little handset on it. And it is an actual device that basically all it does is provide telephone service or real-time audio communication service. So if you look at a Voice over IP telephone, it looks like a telephone.
A soft phone is a piece of software that you install on to a computer to allow that computer to provide real-time audio communications, Voice over IP. So a softphone is a piece of software that gets installed on to a computer or gets installed onto your little iPhone, any of these computing devices. If it’s not normally considered a phone and you install a piece of software on it then it is a soft phone. So soft phones are software that allow computer devices to act as phones. Hard phones are Voice over IP phones that actually look like phones. So if you walk up to it, if it looks like a phone, it talks like a phone, it’s a hard phone basically. If it’s something that you would associate as a phone then it is a phone.
Now, the next big thing to understand with the Voice over IP is these are all computing devices. So whether it’s your iPhone, whether it’s your computer, or whether it’s this hard phone that we’ve been talking about, these are all computer devices. The dumbest, dumbest, dumbest Voice over IP hard phone is light years ahead than any phone that ever connected into any of the original PBXs. So if you have a normal telephone, if you have a normal telephone that plugs into a normal PBX in a normal telephone system, that device is dumb. There’s not a whole hell of a lot to it. If you understood how to put parts together, you could probably build one in your home, right?
A hard phone is actually a computer device that looks like a phone. So this hard phone is actually a computer and when you go in to configure hard phones, so these are phones that look like phones, you will actually do so through a web interface. So I use to love the Polycom hard phones. You would go to the IP address for that phone. When you open it up, there is a little web browser because that little thing is actually a web server and you would configure everything through the web server that resides on that hard phone. So like I say, these things actually do have brain power. These – even the hard phones are computers that simply look like phones.
Now, the final thing to talk about with these Voice over IP clients or devices because like I say, it can be an iPhone, it can be a computer, it can be a hard phone, it can be any number of things, is that these devices connect to accounts within the Voice over IP server. So in the Voice over IP server, you set up the user accounts like you would in most other servers. So if you’ve dealt with Windows servers or Linux servers, it’s kind of the same way.
So in this Voice over IP server, if you’re setting up let’s say extension 105, you would say, “Extension 105, the username is X and the password is X.” And then you would set a whole bunch of other configurations. So if you are configuring an account in the Voice over IP server, there are probably 10 or 20 different configurations that you can do. But the big ones to understand is that you plug in the extension, you plug in a username and you plug in a password.
Why I say these are the most important things is because for a Voice over IP client, you then go to the client whether it’s the iPod or iPad, whether it’s the computer or whether it’s this hard phone, and inside, even the hard phone you say, “This phone is extension 105 with a username of X and a password of X.” This is very important.
In the old PBXs, everything was configured inside the PBX itself. With a Voice over IP (VoIP) server, you now have a client server connection so you create the user account within the Voice over IP server and then for the device that will be connecting, for the client that is connecting, you have to give it the information it needs to provide the Voice over IP (VoIP) server.
So what will happen is you plug in this information, extension 105 username X, password X. When this phone gets on the network, it will connect to the Voice over IP (VoIP) server and it will say, “Hey, my username is X and my password is X. I want extension 105.” And the Voice over IP will say, “OK, your username and password are correct. Here, you are now extension 105.” So if somebody calls in from the outside world, the dial extension 105, they will now go to this phone. Like I say, it’s all pretty simple. The same thing with the little iPhone. If you need extension 106, you will plug in 106 to the iPhone, username X, password X. And so if somebody called in for 106, it will go here.
The very important thing and this is where you have to be careful about with VoIP, it’s not complicated, it’s none of that, but understand, if you make a mistake and you put username Y password X or you do username X, password W, if that is not the correct username and password combination this Voice over IP server is not going to allow you to get the extension. So that is something that’s very important to understand. So with these Voice over IP clients, like I say, these are now clients, these are computer devices that connect to a Voice over IP server. Hard phones are computers that are built to look like a phone. They are still computers but they are built to look like phones.
Soft phones are pieces of software you install into normal-looking computers to make them act like a phone. So like I say , if you have a normal computer, you have a normal laptop computer, you have netbook computer, you have an iPad or an iPhone, you would install a soft phone on to it and that allows that computer to now connect to the VoIP server and allows that computer to now act like a telephone.
One of the biggest things and the biggest things that I’ve seen that causes people to have problems in the real world is understand within this Voice over IP server you are now going to create user accounts just like you would create like I say for Windows server, for Linux server, etc. You are going to tell it the extension, you are going to tell it the username, and you are going to tell it the password plus about 20 or 30 other things.
The biggest point is this device out here you will have to go in and you will have to configure within that device and say, “I want extension 105. The username is this and the password is this.” If any of this is incorrect, the whole kit and caboodle is not going to work. So this is Voice over IP clients in a nutshell. Like I say, it’s not too complicated as long as you can follow all these little lines.
So we’ve talked about the servers, so the Voice over IP servers, these are servers that provide services to other computers on the network. Those other computers are Voice over IP clients. Those clients can be either hard phones or soft phones. They are all computers. Like I say, even that thing that looks like a phone is not a phone. It’s actually computer that looks like a phone. They all communicate. There are usernames, passwords, etc.
Voice over IP (VoIP) Gateways
Now, the next biggest component and really the only other major component in a Voice over IP network are the gateways. The gateways are what connect different types of communication networks. So way back in the day, the gateways really all they did was they turn Voice over IP communications into normal telephone calls. So what would happen in the old days is you would have your Voice over IP server and let’s say you are on the internal network and you if you made a call from this phone here to this phone right here, it was all IP. It was all Voice over IP. So I would call into the Voice over IP server and then that would route the call to the other Voice over IP phone.
Now, here’s the question. What if Bob is out here in the house? So he has a normal telephone with normal telephone lines, etc. He doesn’t have a Voice over IP (VoIP) phone. So what they did is they created these things called gateways. So a gateway, what would happen is if you were calling to an outside line, what these gateways did is they had normal RJ11 telephone connectors on them so you could connect a normal telephone line from the outside world into one of these gateways.
So the telephone line that you have in your house you could connect into one of these gateways. So that gateway would then connect to a normal telephone line and then you could call into Bob’s house. So basically what would happen is if you call from your Voice over IP phone, that would get routed through the Voice over IP server, that call would then get routed to a gateway and then that gateway would send the phone call out on a normal telephone line. So the normal, like I say, the normal telephone poles, telephone lines, etc, these gateways connected between the Voice over IP world and the normal telephone world.
Why this was important way back in the day when I was first learning about Voice over IP 10 whole years ago, is because when you work for enterprise companies, see enterprise companies have lots and lots and lots of offices so you may have your one office here in Middle America like the first company I worked for, but then you have a thousand or actually let’s say they had 60 different offices all over the country, so they already had to pay for internet connections, T1 connections, to all of their remote offices regardless. So they open up a remote office, they already had to have an internet connection to each one of these remote offices.
Now here was the thing. If you have your billing department, so what we did, we billed customers, we billed lots of residential customers, right? So if that residential customer is sitting right down here, your billing department, so our installation department was here, our installation department was 20 miles away from where that customer lived. But our billing department was all the way back here in Middle America. So if our billing department wanted to call this customer, it would be a long distance charge. And again, when you are dealing with one or two people, this isn’t a big deal. But when the customer service and the billing department is a hundred people, that’s a whole bunch of money. So every time they had to call a customer whether it’s here, whether it’s here, whether it’s here, whether it’s here, whether it’s here from Middle America, it is always a long distance call. So they were always getting charged.
So the initial idea so you understand how Voice over IP works, and this is still how Skype and all these companies work, is what they said is here in our office, we are going to have Voice over IP phones. So we are going to have phones that use our network connections, our internet connections. And then here at this remote office, we are going to put in a gateway that allows us to call local numbers. So there’s a Voice over IP server here and a little Voice over IP server here, this server connects to a gateway, right? So now, when our billing department decides to call this person that’s here, what will happen with the Voice over IP traffic is it will get sent over this T1 line down to the Voice over IP server that’s sitting in our building here, it will get routed as gateway and from this gateway, it is a local telephone call to that client.
So basically, every office had to have telephone lines anyway. In order for them to do business, they had to have telephone lines. They already had to pay for these T1 connections that cost them $500 or $600 a month. So all they did is they installed a Voice over IP system and then whenever they had to call one of these people, instead of having to make a long distance call, so instead of having to make a long distance call from Middle America all the way to Seattle, the call would get routed through the T1 connection they already had to their Seattle office. From the Seattle office, it would get – the call would get sent out in gateway that had a local telephone number on it and then call that client. And that saved people a lot of money.
So what is gateway? So the original main thing that they did was they connected the Voice over IP network to a normal telephone network. So a normal telephone, a telephone pole, etc. So that was the main thing with these gateways especially with large companies and when you’re thinking about companies like Sears or JCPenny or Exxon or any. They have thousands of facilities all over the country or all over the world. They could route their telephone calls through the internet connection they already had and then pop out and make a local phone call. Made pretty simple. Now, gateways are used for a little bit more but it’s still basically simple as far you are concerned. So now that there are services such as Skype, such as other like Voice over IP services, there are now gateways specially designed so that Skype Voice over IP traffic can now be turned into normal or SIP Voice over IP traffic. We are going to talk about this in a second.
So gateways are still used. They are either used like I say, to connect to the normal telephone lines or for things like if your company or the company you are using is already using Skype phone numbers, you can have a Skype gateway that now will connect you to a SIP Voice over IP system. So these gateways connect different types of communication networks basically. So whether it’s Skype to SIP, whether it’s SIP to telephone, whether it’s telephone to Skype, etc, gateways are what connect these different types of communication infrastructure.
So we talked about servers. We talked about the clients. Now, we talked about the gateways. So those are the major components of the network. That’s what you’re basically going to go and buy. You buy a Voice over IP server or you will lease one from somewhere. You will buy Voice over IP clients. You will buy gateways, etc.
Voice over IP (VoIP) Protocols
Now, we need to talk about how those devices communicate. So when you make a phone call from one person to another person, how is that communication done? Well, Voice over IP communication uses protocols. So you probably know of TCP/IP or Apple uses Bonjour or NetBIOS, etc. Well, Voice over IP uses protocols in order for the communications to happen. So this is just a network language. Now, the standard protocol that I would say you should try to buy system that use is something called SIP. SIP stands for Session Initiated Protocol. So this is the ratified protocol that lots and lots and lots of companies use. So you can buy Cisco SIP phones. You can buy Polycom SIP phones. You can buy Asterisk SIP phones. So SIP is a protocol that lots and lots and lots of vendors have implemented.
So what I like in my little world is I can buy a Voice over IP server from one manufacturer and I can buy SIP phones from other manufacturers. So if I want really expensive SIP phones, I would buy Cisco SIP phones. If I want really cheap SIP phones, I would buy Linksys SIP phones. Basically whatever my budget allows, is what I can afford. So this is the protocol. It uses SIP. SIP resides on top of TCP/IP. This is actually an application layer networking communication so this can ride on TCP/IP. This can ride on UDP. This can ride on some other protocols. So this is actually – it’s a networking protocol but it resides above TCP/IP. So SIP is the basic communication that like I say, the Voice over IP servers use, the telephones use, etc. This is how they talk to each other.
Now, why I say SIP is important? SIP. SIP. SIP. Have you heard me say SIP before? SIP is very important and you should buy systems that use SIP as the protocol. Here is the reason why. It is because some of the major manufacturers of telephone systems, they don’t really like open source. If you buy an Avaya phone system, they want you to buy Avaya. If you buy a Nortel system, they want you to buy Nortel phones. Avaya doesn’t want you to buy an Avaya system and then Cisco phones or an Avaya system and Linksys phones. Avaya wants to sell you both the telephone system and all phones, the call boxes, etc that go with it. OK. It’s a fine business practice for them, but I hate it.
The way they are able to make this happen is they have their own proprietary protocols that nobody else can use. So don’t quote me or don’t sue me if you’re from Avaya. But the last time I was looking at Avaya phone systems, like I say, back in the day, I was certified 90 hours of certification on Avaya phone systems. I think Avaya phone systems are just the cat’s meow, they are very high quality, they are very basically user-friendly, etc. When I went to buy Voice over IP systems for my clients, I found out that they only use proprietary protocols now. So that kind of killed it for me. I’ve never used an Avaya phone system again. Why? Because if you buy an Avaya Voice over IP PBX or Voice over IP server, you can only buy Avaya phones to communicate with it because Avaya doesn’t license out this protocol just willy-nilly. Again, they want you to buy the phone system and the phones all from them. No, I think that’s a bunch of garbage.
That’s the other reason why I was just talking about the gateways and for Skype, Skype uses a proprietary protocol. So if you use the Skype service, you can’t go out and buy just any willy-nilly Voice over IP phone to connect to the Skype service. That phone has to have the Skype protocol built into it. Again, that’s why I like SIP lots and lots and lots and lots and lots and lots and lots and lots of manufacturers build staff for SIP. And like I say, I just think it’s the future and if you buy something non-SIP I just think that’s kind of dumb.
The nice part with SIP is what’s good for you as a consultant or you as a business person, I’ve seen this. Since Cisco deals with SIP and open source Voice over IP servers deal with SIP, I have seen fellow consultants where what they will do for clients, if clients want to seem prestigious, if they want to seem more important than their bank account actually allows, what the consultants will do is they will go out and they will buy Cisco SIP Voice over IP phones and then have those phones connect back to a free open source Voice over IP server. So it looks like they have this really expensive fancy Cisco system, when really all those Cisco phones connect back to a little $400 computer sitting in the back room closet somewhere.
So this is something that you can do that makes SIP nice. You can have Cisco call manager connected to the Linksys phones. You can have Cisco phones connected to the Asterisk. Since SIP is the networking protocol that allows all these devices and Voice over IP servers to communicate, you can mix and match at will. So that’s very important. Like I say, Nortel, Avaya, a lot of the old fashioned telephone manufacturers use proprietary protocols and I’m telling you it’s a bad, bad, bad, bad, bad, bad, bad, bad idea to use those because you can either use stuff from everybody or the proprietary stuff.
Now, we’ve talked that all these Voice over IP devices and Voice over IP server use a protocol to talk to each other. So this isn’t TCP/IP. This is either SIP or it’s a proprietary Skype protocol or proprietary Avaya protocol but they all use a protocol in order to communicate to the server and to other devices on the network.
What is a CODEC & How Does It Apply To VoIP?
The next thing we need to talk about are the Codecs, C-O-D-E-C, if you can’t read that. The codecs, this is how the voice traffic is actually encoded and encapsulated. So when you are talking on the phone, your communication has to get put into little packets and sent down the network. Your codec is what determines how this happens. So if you want really high quality communication Voice over IP traffic and you have a lot of bandwidth then you will use a codec that uses a lot of bandwidth and you have high definition audio communication back and forth. But let’s say you’re on a kind of crappy network, you don’t have a lot of bandwidth on the network, your codec is what will determine and you can say, “I want to use a lesser grade codec where our communication is not going to sound as good but it will use less bandwidth.”
So the main thing with codecs that you have to remember is codecs determine the quality or sound actually I should say, sound quality of the conversation. So how much static is on the line, is this high definition audio communication or is this something that sounds like you’re on a CD? That is determined by the codec you use and then also, the bandwidth that is used for the communication. So the codec determines the quality of the sound and then how much bandwidth is being used when you talk to somebody over this Voice over IP (VoIP) network. So when you pick up the phone and you call Bob in the office, five offices down, how much bandwidth is that communication going to take? Is it going to take 10 kilobytes per second? Is it going to take 4 kilobytes per second? It’s all determined by the codec that you are using. So this codec is basically like I say, it’s what encapsulates and it determines the sound quality and the bandwidth used.
Now most of you if you are dealing with small offices with pretty good networking gear, you don’t really have to worry too much about the codec. So whatever Voice over IP server you use will have codecs built in. Some codecs are proprietary which means you have to pay money in order to use codec. But when you buy your server, you will either get a license to use that proprietary codec that is there or they will give you open source codecs to use.
So like I say, if you download Asterisk or Switchvox or sipX, they have open source codecs already built into it so you can just use those codecs for your Voice over IP communications. No problem. The only issue is of course, being open source, they are not necessarily the best codecs that you can be using. So the sound quality is probably going to be pretty good and it will be probably more than what you need but the bandwidth used is going to be more than some of the better proprietary codecs out there.
So basically whenever you pick up the phone, the sound quality will be fine but each telephone call is going to take more bandwidth than necessarily is needed. Now, if you are dealing, like I say, if you are dealing with a hundred people or a thousand people on a network, you have to worry about network congestion because if you have a thousand people on a network and 50 people are on the phone, all those little 10 kilobyte per second Voice over IP communications can start taking up a lot of bandwidth. So what you should think about is if you are dealing with large networks, is you may have to buy a proprietary codec for your Voice over IP system. Normally, they run – I think they are about $5 per device that will be connecting to the network.
So if you are noticing, if you switch over to a Voice over IP system and you notice your bandwidth starting to get constricted, you may think about having to change your codec. Hopefully, you can change your free open source version but if that is still using too much bandwidth, you can change to proprietary codec. Again, you will probably pay about $5 per phone or per device that will be connecting but you can normally get really high quality communications down to about 4.5 kilobytes per second I think is what the good ones used. So basically, these proprietary codecs will give you high quality sound with lower bandwidth. So that’s the codecs. Again, codecs, this is what encapsulates and decides the sound quality and the bandwidth usage of your Voice over IP traffic.
So we’ve talked about the protocols now and we’ve talked about the codecs. The final thing that we need to talk about is a network latency and QoS or quality of service. Now, both of these things I’ve talked a lot about in other classes so I’m going to run through them here just because if you are showing up in the beginning of this will give you the information but we talk about this much more in many of our other networking classes.
Why Quality of Service (QoS) Matters
So the first thing I’ll just run through really quick is quality of service. Again, we’ve talked about this a lot. But what this is used for is since you are now using your network not only for computer communications but also for telephone, for Voice over IP communications. You have to be careful that your computers don’t use all your network bandwidth because if your computers start using all your network bandwidth, you have no bandwidth left for your telephone system.
So if one of the dingbats in accounting decides that they are going to download BitTorrent files, they are going to download pirated movies and they start using all the bandwidth on the network, well then when you go to make a phone call, you are not going to be able to make a phone or the quality will be very, very, very poor because all the bandwidth is being used by that idiot in accounting to download BitTorrent files. Again, once you start – you have a larger and larger company, your percentage or whatever numbers, you get more and more idiots. So when you have a 50-person company, you probably have one or two idiots. When you have a 100-person company, you have 5 idiots. When you have 1000-person company, you hope you only have 50 idiots. I mean that’s kind of how it goes.
So what Quality of Service does is it allows you to prioritize network traffic. So what this means is you go in to your networking equipment, so this is your switches and your routers. And in these switches and the routers, you can prioritize network traffic based on what it is. So basically all you do is in the switch or router, you say, “I want Voice over IP traffic to be much more important than normal computer communications.” So what this means is that your switches and your routers will always make sure your Voice over IP traffic gets through and it’s not so worried about all those computer communications.
Again, when you are sending emails or you are downloading files, a little bit of delay, you don’t even notice it. If you are talking to somebody on the phone and there’s a delay, you start getting weird stuff if there is delay. So the main thing is you don’t want delay on the network. That’s why you use the Quality of Service. And again like I say, it will prioritize your Voice over IP network traffic basically to make sure everything goes through.
The next thing that we need to talk about is network latency. And this network latency is most important if you decide to use a hosted Voice over IP server. So the host of Voice over IP server again is back in the old days and how a lot of people do it, is you would have your PBX or your Voice over IP server in the building where you work. So all your telephones, your computer, and Voice over IP server were on the same building.
Nowadays like I say, that little Voice over IP server can be on the internet and all your computers and devices, etc can connect to that Voice over IP server through the internet. Well, here’s the problem. You need to make sure your internet network latency is not too high. What network latency means is it means the time it takes from when a bit is sent from one place to the next. So when somebody starts talking, when they say hello, how long does it take for those bits to go from that Voice over IP server all the way to your building?
Now, you may not realize or have ever thought about latency until you start using a Voice over IP. The reason is, is because when you are downloading files, you don’t really notice how quickly everything happens. But when you are having a communication, everything has to happen basically real-time. So when I start talking, as soon as I start talking, the person on the other side has to start hearing what I’m saying. When they start talking, I have to start hearing what they are saying. If that doesn’t happen, we start talking over each other like sometimes I’m sure especially with cell calls, you can have a really miserable experience where if the timing is off, you start talking over them, they start talking over you. You don’t really know where you are in the conversation. Why? Because it takes too long for their words to come from where they’re at to where you are.
So basically, network latency is how long it takes for the bits and bytes to get from point A to point B. Now, a normal telephone call as I understand it, look it up on the internet like Wikipedia, has a latency of 45 milliseconds. So when you are on a normal phone call with your wife, your mother, your brother, your sister, your lover, when you start talking, it takes 45 milliseconds for your word to get from here to there. So whether you are talking to them across town or across the country, it takes 45 milliseconds for your words to get there. And so that is considered average call calling, so 45 milliseconds.
Now, in the Voice over IP world, they are a little more lenient about this from what I’ve seen. Basically, depending on who you talk to, you can 75 to 100-millisecond delay and still have a relatively OK communication with the person on the other side. So this means when you start talking, it takes anywhere between 75 to 100 milliseconds for your words to get from there to there. So that’s something to just understand and keep in mind.
We are going to have a network troubleshooting class where I’ll show you how to figure out your latency on your internet connection but just understand like I say, if you are using Skype, if you are purchasing a Voice over IP service on the internet, your network latency is very, very, very, very, very important because if it is over 100 milliseconds, if it takes over 100 milliseconds for your words to get from you to the person you are talking to, you’re going to have an absolute mess. I’m sure you’ve had those horrible phone experiences in the past and it’s just miserable. Like I say, the normal standard is considered 45 milliseconds. A normal telephone call, this is an old fashion telephone call as in you have your telephone at your house, you call your mom, it takes 45 milliseconds to get from point A to point B.
I say with Voice over IP, before you start having really problems, it’s somewhere between 75 to 100 milliseconds. If you understand how to figure out the latency, you will be fine. If you don’t understand how to find out those latency, like I say, come back for the network troubleshooting class and we will talk about this.
How VoIP Works With Unified Communications
So now before we go into the final thoughts, we’ve talked about basically everything we need to talk about for Voice over IP, the final thing that I just kind of want to get into just a little bit though, is something called unified communications. So in the old world, we dealt with telephones. And then we came to Voice over IP. So basically as most of us think of it, Voice over IP is telephones but they use Ethernet and TCP/IP standards.
Well, the idea with unified communications is people are sitting down and they are saying, “Well, if telephones are now basically computers and telephones can talk to computers and the Voice over IP server is a server, what else can we do in the computer realm to make communications easier and to make communications better? And this is where the idea of unified communication comes up. So basically what this is is it’s kind of turning some of these things on their head and basically giving more functionality for communication. So now, since you can have a soft phone on your computer, the idea is why not install an Outlook plugin so straight from Outlook you can make a phone call?
So let’s say, somebody emails you a message, instead of emailing them back, you can click on their name, your computer can now make a call through that Voice over IP server. When it connects, you hear the people or you hear the person you are calling through your speakers and you are talking to the person through a little microphone that’s sitting on your computer. So now, your computer is acting as a telephone. And not beyond that, you are actually calling straight through Outlook so you don’t need any additional soft phone software out there.
Or the idea of let’s say, while that conversation is happening, you can have Outlook actually transcribe and write down everything that is being said especially a lot of the people are worried about legal issues, what got said, when did it get said. If you have an audio file, it’s very hard to go back and dig through all of that. If all of that gets written into a text file, you can do a Google search anytime you want to see when things are said. So while you are having this communication, the text can be transcribed.
You have probably already seen with unified communication where if somebody sends you an email, you can have that turned into an audio file and sent to you as a voicemail. So somebody sends you an email, a computer reads it, turns it into a sound file and then you get a little voicemail on your telephone, you pick it up and goes, email from Bob Jones, “Hello! It was nice to meet you today.” That’s a function of unified communication.
Or the idea of if you don’t want to get bothered with picking up voicemail and such, people can call to your voicemail. When the phone – when the call gets recorded on to the voicemail system, your Voice over IP server can turn that audio file into a text file. So now, you call in, you leave a message, the computer turns all of that into text and then emails it to you. So instead of having to call in and get your voicemail, you now just get an email sitting in front of you.
Other features that they are talking about is things like instant messaging. You deal with AOL or ICQ. And if you want to have an audio communication with somebody, they would have to be using AOL Instant Messenger or ICQ or such. Now, the idea is you will just have this one instant message in your client and if you want to call somebody to a normal telephone line , if you want to call somebody using a different type of system, you can just click on them and you will be able to make that call through.
These are all the concepts of unified communication. Like I say right now, this is a conceptual thing. This is where we are going to. This is where we are moving to. The idea is now in the past as we talked about before, telephones were silo-ed in their own world. Computers were siloed in their own world. They could talk a little bit but they really couldn’t talk too much. Now that we are using Voice over IP, “telephones” now reside in the same world that computers reside in. So now, how can we get them to talk? How can we get really cool information to go back and forth and just make everybody’s life easier? It’s a pretty cool concept and it’s something you should keep your eye on.
So that was a class on Introduction to VoIP. Hope you’ve been able to follow along with us pretty well. Again as I always say, this stuff is relatively simple as long as you understand what’s going on. We talked about the Voice over IP servers. So Voice over IP servers act like the old telephone system PBXs did. Like I say, I call them Voice over IP servers because these are computers that provide services to other computers on the network. As we talked about with the Voice over IP clients, every Voice over IP client is a full-pledge computer. If you know how to hack it, you can probably start playing Space Invaders. Even on a Voice over IP telephone, they are all computers. You actually can figure them by going into a little web server interface that resides on the little telephone or the device. It’s really true.
We talked about the hard phones. So hard phones are these Voice over IP clients that look like a phone. They look like a telephone but they are really a computer. But we call them hard phones because basically they are single-used devices. Although they are a computer, all you use them for is for telephone calls.
We then talked about soft phones. Soft phones are pieces of software you install on to normal computers like a computer, a laptop, a netbook, even an iPhone and that allows you to connect to your Voice over IP server and use that computer just like you use a telephone.
We talked about the gateways. So gateways are what connect the Voice over IP world to the normal telephone world. So like I say, you have normal telephone lines that come in. They come in to one side of the gateway and then your Voice over IP connection comes into the other side of the gateway. If you need to call to the outside world, that gateway allows that Voice over IP traffic to get to the outside world.
We talked about the protocols. Like I say, protocols are very important and if I haven’t said it enough, just remember SIP, SIP, Session Initiator Protocol. SIP is a standard protocol that lots and lots of manufacturers and vendors use for their Voice over IP servers and Voice over IP clients. Again, you can mix and match devices and servers. You can put a Cisco Voice over IP phone on to an Asterisk free open source Voice over IP telephone server with the other manufacturers. Like I say, Avaya, Nortel, etc. A lot of them use proprietary protocols, which means if you buy an Avaya phone system, you have to buy Avaya phones. There’s no – I have – it’s my opinion, I have not seen any quality improvement. I have not seen any good argument on why you should stick with one manufacturer. It’s not like if you buy only from one manufacturer, the equipment is just so amazing. I mean all of the phones and all of Voice over IP systems are very good. So I would say just stick with SIP.
We talked about the codecs. So the codecs are the pieces of software that actually encode your audio communications. So this is what determines the sound quality and the bandwidth used when you are on a Voice over IP call. So when you pick up the phone and when you start talking, that codec is what turns your communication into the packets to get sent off.
Now again, when you buy a Voice over IP phone system, they will come with codecs and normally they are fine. Like I say, your free open source phone systems come with free open source codecs and by and large they are fine and therefore you really shouldn’t worry about it. If you are noticing bandwidth congestion or if you are noticing other problems, there are proprietary codecs that you can purchase and install on to your Voice over IP server that have better performance. So instead of using 10 kilobytes per second, it will use 4.5 kilobytes per second. Again, most of the time this doesn’t matter especially for small networks but when you are dealing with a hundred or a thousand or ten thousand users, that can really matter. Generally from what I’ve seen, it’s about $5 per device or per client for these codecs. So that’s where you are looking at paying for.
We talked about the network latency and we talked about QoS or Quality of Service. Network latency is important especially when you are using a hosted Voice over IP service. So latency is the – how long it takes from a bit to get from where you are at to where it’s going. So when you are talking to your mom, a normal telephone call, it is 45 milliseconds from when you start speaking to when she hears it. With Voice over IP, they say somewhere between 75 to 100 milliseconds is OK. It’s considered good sound quality.
If you have more than 100 milliseconds in delay between when you start talking and when they hear you, you start talking over each other because you start talking, they haven’t heard you so they start talking. I know if you ever used a cell phone, you get this every once in a while where there’s just a mismatch in the communication so you start talking but they haven’t heard it so they start talking over you and then you start talking over them and it’s just a mess. So this is network latency. And then as we’ve talked about a lot, a lot, a lot is QoS, Quality of Service and basically this is that your network packets are prioritized based on what type of traffic they are. So make Voice over IP traffic far more important than normal computer traffic and you will be good.
Finally, we talked about the overall idea of unified communications. So this is where everything is going. Since we are now at Voice over – we now have Voice over IP, so we have something – we are in something called convergence. We had a class on convergence. So telephones now use the network, TCP/IP network. You can now have computers talking to telephones and audio communication and you can get a bunch of really cool fancy things. You can get instant messaging systems that you can make a telephone call through.
So back in the day, you could do an instant message audio call where if you’re on AOL Instant Messenger and somebody else is on AOL Instant Messenger, you can make an audio call to them. Well now since it’s unified, through AIM or through some instant messaging service, you can actually make a call all the way out to the outside world. You can call whoever you want. If you are sitting in Outlook, you can make a call straight through Outlook and the call will be coming through your computer speakers and you talk into your computer microphone.
So the idea with unified communications is everything gets unified. So again like I say is if you are looking at the Outlook scenario, we all know about inboxes, we all know about sent messages, etc. Now imagine if Outlook can actually record the phone call that when you are talking to somebody. So when somebody calls you, you would automatically record that phone call in a file and keep it in your inbox or if somebody leaves you a voicemail, that file will be sitting in your inbox. Those are the types of cool things that can be done with unified communications.
So this is a class on Introduction to VoIP or Voice over IP. This is the basic high level concepts and how it works. As you know, I’m Eli the Computer Guy. It’s always fun to teach these classes and I look forward to seeing you with the next one.
About Fastmetrics, Inc. Building & Business ISP
Since 2002, Fastmetrics is the Bay Area’s only dedicated business ISP. We provide telecommunication services in California and the San Francisco Bay Area. Reliable service – backed by better live and local support. From install to 24-7 proactive monitoring, get treated like a VIP customer. Not a number by a faceless call center. We specialize in managed business internet and phones, dedicated high speed business fiber internet, business WiFi, SIP voice solutions / UCaaS and managed network services. We are a Microsoft and Cisco Meraki Partner. Our team are Certified Cisco Specialists, Ubiquiti Enterprise Wireless Accredited and Polycom Authorized Solution Advisors. We take care of your business network, so you can focus on growth.